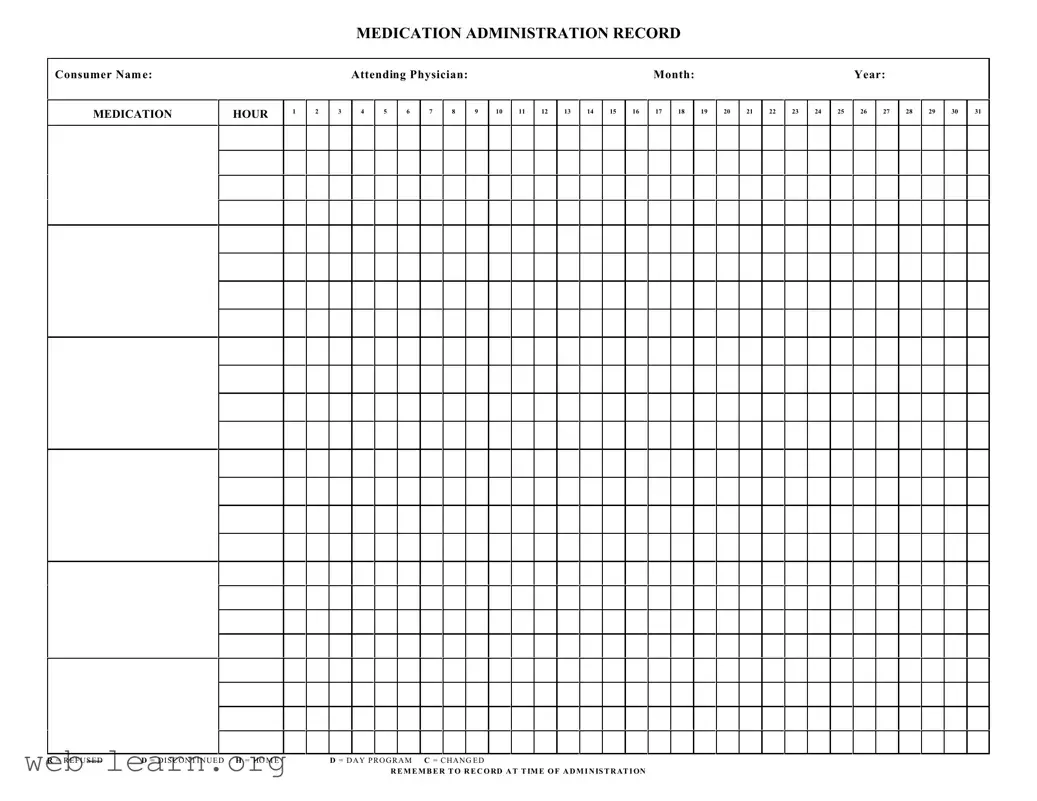
The Medication Administration Record Sheet is an essential tool in healthcare settings, particularly for ensuring the safe and effective administration of medications to patients. This form captures vital information, including the consumer's name, attending physician, and relevant dates, allowing healthcare professionals to track each medication administered throughout the month. Organized into a grid format, the form includes designated hours for medication intake, noted by numbered columns that facilitate easy reference. Each day features specific designations, such as 'R' for refused, 'D' for discontinued, 'H' for home, and 'C' for changed, to ensure clarity in medication management. It serves not only as a record of what has been administered but also as a prompt for healthcare providers to document thoroughly. Proper usage of this form is critical; it requires diligent recording at the time of administration to maintain accurate medication histories and avoid potential errors. By following the established protocols outlined in the form, caregivers can enhance the quality of care while providing a reliable reference for ongoing treatment decisions.